Good governance, including honest and transparent operations, is fundamental for PLANB's sustainable operation and growth. The company adheres to principles of good governance and business ethics to ensure fairness and instill stakeholder confidence.
PLANB has established a business structure, management system, and governance framework that aligns with the good governance principles of the Stock Exchange of Thailand, the Securities and Exchange Commission Office, the recommendations of the Thai Institute of Directors Association, and various international standards.
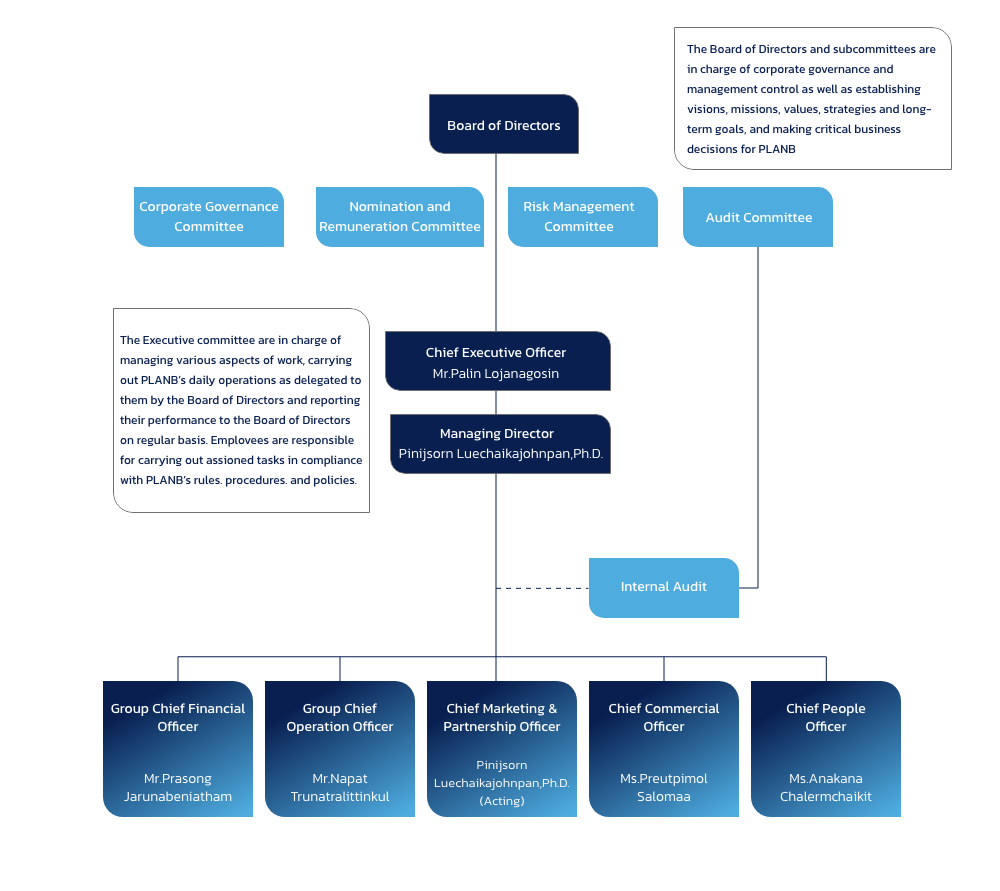
To enhance transparency and governance efficiency, the Company disclosed information regarding the Board of Directors’ meetings in 2025, which were convened a total of six (6) times, comprising two (2) physical meetings and four (4) hybrid meetings (combining in-person attendance with electronic participation). The Board members attended all meetings in full, reflecting a 100% participation rate, which demonstrates their commitment and accountability in carrying out their responsibilities diligently.
In addition, the Board of Directors has ensured that the Company’s operations align with good corporate governance principles in all dimensions—ranging from accountability to shareholders, respect for stakeholders’ rights, adequate and transparent disclosure of information, to the maintenance of independent oversight. These mechanisms play a crucial role in elevating the Company’s governance standards, thereby fostering resilience, transparency, and the creation of sustainable value for both the organization and its stakeholders.
The Board of Directors conducts an annual self-assessment to serve as a framework for evaluating the performance of the Chief Executive Officer, the Managing Director, and the Board as a whole. The process also includes a review and compilation of observations and feedback on matters related to the Company’s operations and the performance of duties during the year, with the results reported to the Board of Directors on a yearly basis.
For the year 2025, the performance evaluation of the Chief Executive Officer and the Managing Director achieved a score of 97.78 out of 100, reflecting their strong commitment, capability, and highest sense of responsibility toward the organization.
Further details on the evaluation results are disclosed in the Annual Report and the Sustainability Report
Plan B recognizes that transparent business operations and adherence to sound business ethics are essential to driving sustainable organizational development and building trust among all stakeholder groups. In line with this commitment, the Board of Directors has developed and implemented the “Corporate Governance and Business Ethics Handbook” to serve as a code of conduct for directors, executives, and employees at all levels, including those of the Company’s subsidiaries. The handbook outlines key principles and standards in the following areas:
- Human Rights
- Fair treatment of business partners and competitors
- Appropriate interactions with government officials
- Social and environmental responsibility
- Occupational health and safety
- Anti-corruption and bribery prevention
- Anti-money laundering
- Appropriate conduct in political activities
- Protection of intellectual property rights
- Confidentiality and personal data protection
- Insider trading prevention
- Conflict of interest management
- Whistleblowing and complaint mechanisms, including disciplinary actions in cases of violations
All directors, executives, and employees at all levels have signed to acknowledge and confirm their compliance with the Corporate Governance and Business Ethics Handbook. This serves to strengthen a corporate culture rooted in transparency, accountability, and alignment with international standards
| BUSINESS ETHICS TRAINING (%) | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Employees Attended Training | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Employees Passed the Assessment | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Average Employee Score | 100 | 100 | 100 |
In 2024, the Company did not encounter any disciplinary violations related to business ethics. The details are as follows:
| VIOLATION OF BUSINESS ETHICS | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Total number of reported business ethics violations: | |||
| - Number of cases currently under fact-finding investigation | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - Number of cases under investigation | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - Number of cases that have been resolved | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Business ethics violations are categorized by type: | |||
| - Regulatory non-compliance | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - Corruption, bribery | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - Privacy violations | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - Discrimination | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - Sexual harassment | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - Harassment | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - Conflicts of interest | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - Money laundering or insider trading | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| - Other types | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Plan B places strong emphasis on enhancing employees’ understanding and ability to consistently adhere to the principles of good corporate governance and business ethics. All new and existing employees are required to complete training on the Company’s governance policies and practices, followed by a post-training assessment. In 2024, all employees—across all levels, from executives, managers, and supervisors to operational staff—successfully completed the training and achieved a 100% pass rate on the assessment, demonstrating full compliance with the Corporate Governance and Business Ethics Handbook.
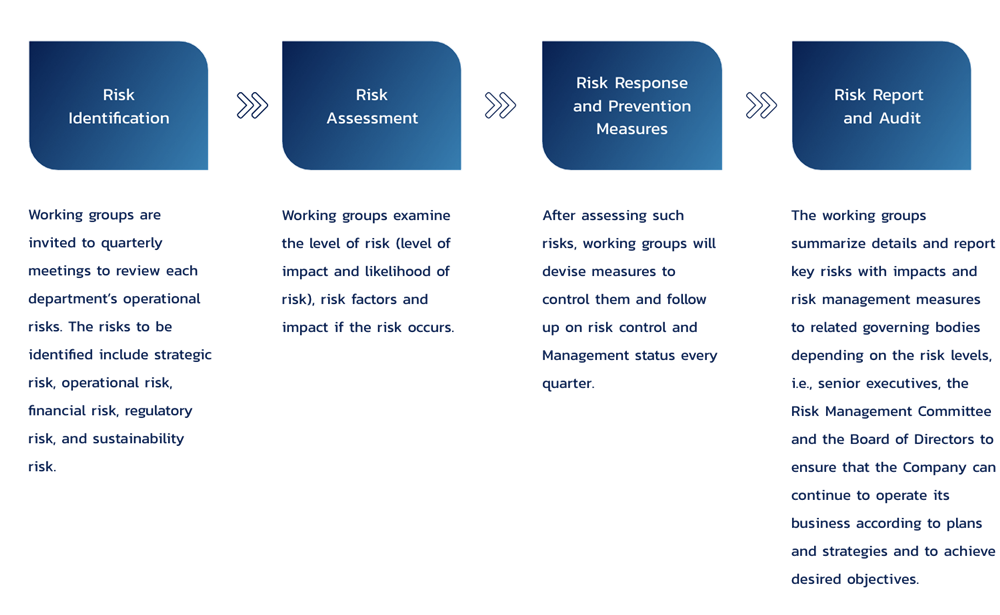
The Company recognizes risk management is crucial because it faces various risks, including commercial, asset, legal, environmental, health and safety, business disruption, and climate change. PLANB utilizes an integrated approach to collecting and analyzing data to identify and prioritize issues, using information from stakeholders operating across multiple dimensions of the value chain. This includes insights into the advertising industry's direction and trends in sustainable development. Prioritizing risks is critical in maintaining PLANB's sustainable business operations.
The Company has established an enterprise risk management framework based on the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) framework, which is implemented organization-wide through its risk management policy applicable to employees at all levels. The Company’s Risk Management Committee (RMC) is responsible for formulating the enterprise risk management policy and framework, and for overseeing risk control in accordance with the defined policies and guidelines. At the same time, the Risk Management Department supports the execution of risk-related activities, including data collection, training, and the promotion of a risk-aware culture throughout the organization.
The Company has a risk management policy that covers all internal and external business activities. This may affect business operations both directly and indirectly. The risk management plan has been effectively implemented since strategic planning. Performance Investment decisions for new businesses, including control and monitoring to keep the risk acceptable. Therefore, the scope of authority and responsibilities of the Risk Management Committee are as follows:
Formulate and review risk management policies and frameworks.
Supervise and promote the organization's risk management practices to align with its business strategies and goals, including the changing environment.
Provide suggestions, monitor, and evaluate risk management practices for the Risk Management Department to implement and execute.
Review the risk management reports of the Company and provide opinions on possible risks, including risk mitigation plans and risk management system development, to ensure effective risk management.
Support all related tasks and executions to meet the Company's risk management objectives.
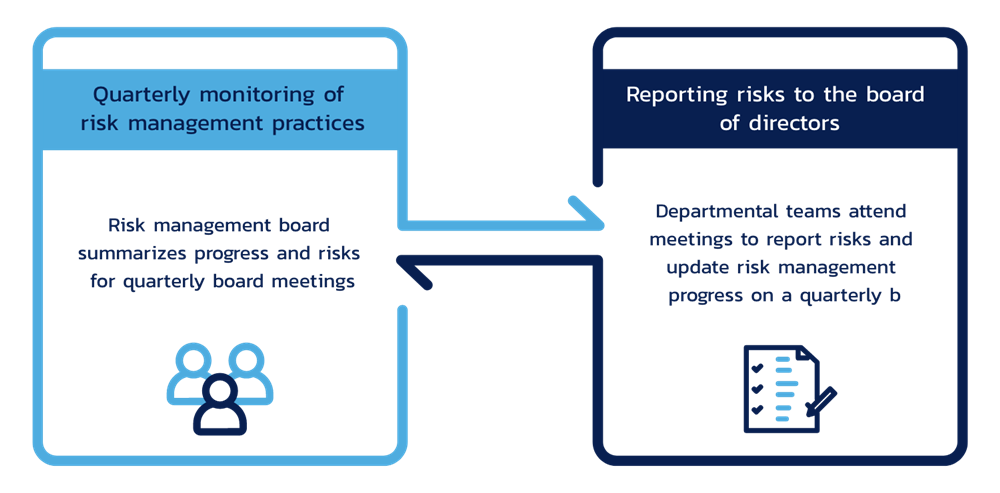
Report risk management performance to the Board of Directors. If a factor or an incident significantly affects the Company's business operations, the Board of Directors must be notified for further deliberation and immediate action.
Consider and approve investments in foreign countries.
Perform any duty as assigned by the Board of Directors.
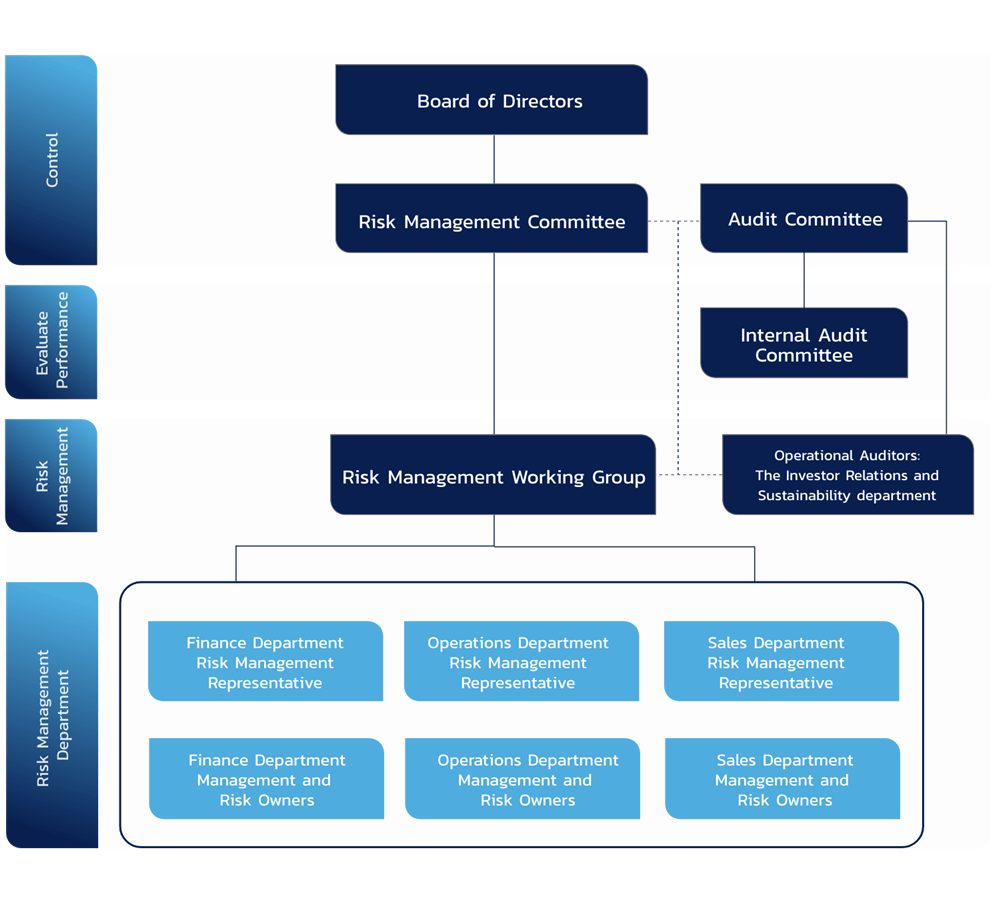
As of 31 Dec 2024, The Company’s Risk Management Committee consists of 4 directors, namely:
- Mr.Mana Jantanayingyong, Director, Member of Audit Committee, and Chairman of Risk Management Committee
- Mrs.Monluedee Sookpantara, Director, Member of Audit Committee, Member of Risk Management Committee, and Member of Nomination and Remuneration Committee
- Pinijsorn Luechaikajohnpan, Ph. D, Director, Member of Risk Management Committee, and Managing Director
- Mr.Arnon Porndhiti, Member of Risk Management Committee, and Member of Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee
The Investor Relations and Sustainability department will review operational practices after meetings with representatives from the Risk Management department to screen risk levels for each topic. This involves identifying topics with high or very high risks and forwarding them to the Risk Management Committee and the Company's board for discussion to develop mitigation strategies jointly. Additionally, the Investor Relations and Sustainability department will track the risk management processes of each department quarterly. This ongoing monitoring ensures that the Risk Management Committee and the Company's board are well-informed and can respond appropriately to evolving risks.
| RISK FACTORS | RISK DETAILS |
| Strategic |
|
| Operational |
|
| Financial |
|
| Regulatory |
|
| Sustainability (ESG) |
|
| RISK LEVELS | ACTIONS | REPORTING |
|---|---|---|
|
Very High |
They must closely monitor and propose an action plan to reduce the risk level, including a monitoring plan to ensure that it is down to a medium or low level. They must propose the action plan to the Board of Directors |
Board of Directors: BOD |
|
High |
According to the business plan, monitor and propose an action plan to the Risk Management Committee (RMC) for approval to bring risks to acceptable levels, including a monitoring plan to ensure that risk level is down to a medium or low level |
Risk Management Committee: RMC |
|
Moderate |
Apply routine control procedures and risk surveillance |
Chief Executive Officer & Managing Director |
|
Low |
Apply routine control procedures without risk surveillance |
Working team |
As over 50% of out-of-home advertising revenue is derived from digital media, the Company has implemented policies to mitigate the risk of losing digital media clients. All sales team members are required to be well-prepared with up-to-date company information and in-depth knowledge of products and services, enabling them to provide timely and responsive support to clients. Additionally, the Company encourages the sales team to cross-sell products and services across other media platforms to compensate for any potential decline in digital media revenue. Regarding risks associated with macroeconomic volatility and slowdowns—factors beyond the Company’s control—the Company addresses them by ensuring that all sales personnel remain consistently proactive, stay informed on industry developments, and regularly present new ideas to clients.
Furthermore, the Company has established additional risk management measures to address rapidly changing consumer behavior and technological advancements. These include continuous monitoring of consumer trends and industry competitors, developing new products and communication channels to diversify media offerings, and conducting integrated strategic risk assessments in conjunction with the annual business planning process. This enables the Company to adapt strategies promptly in response to changing circumstances.
The Company recognizes the importance of effective operational risk management. The Board of Directors has established the operational risk management policy and framework, and appointed the Risk Management Committee to provide guidance and recommendations to management, ensuring that the Company’s operational risk management processes are appropriate for its business context, aligned with international standards, and effective in controlling, preventing, and mitigating risks within acceptable levels (Risk Appetite). Key components of this framework include the development of systems for measuring, monitoring, controlling, and reporting operational risks; the implementation of internal control systems for managing such risks; and the maintenance of capital reserves to absorb potential operational losses. These measures are designed to ensure that the Company’s operational risk management is effective and proportionate to its business operations.
- Risk Identification: The Company identifies risks related to its operations at least once a year or whenever there are changes in operational risk factors that could impact the business.
- Risk Assessment: The Company measures the risk levels of identified operational activities by assessing the likelihood/frequency of risk occurrence and the impact of the risks to evaluate the severity of potential damages.
- Risk Monitoring: The Company monitors operational activities and events that could potentially damage the Company, allowing for timely prevention and control of such incidents.
- Risk Control and Mitigation: The Company has clear risk response processes aligned with its Risk Appetite, including ongoing monitoring, risk management evaluation, and reporting to management and the board. Risk control measures include purchasing insurance and utilizing support services from business partners.
- Risk Data Storage and Reporting: The Company maintains and reports operational risk data to inform relevant parties about risk trends and changes, enabling timely preventive, control, or mitigation actions.
- Business Continuity Planning: The Company has a business continuity plan to cope with incidents caused by uncontrollable factors such as natural disasters, terrorism, and public utility problems. This plan allows the business to resume normal operations according to the Company’s Business Continuity Management Policy.
Regarding the risk associated with reliance on major customers, the Company cannot guarantee that these customers will continue to purchase its products consistently and/or in the same volumes as they currently do. Therefore, if one or all of these major customers reduce their orders or cancel their purchases, it could significantly impact the Company's operations. To mitigate this potential risk, the Company has implemented the following risk management plan:
- Commitment to Building Strong Customer Relationships and Satisfaction: The Company is dedicated to continually improving the quality of its products and services to enhance relationships with these key customers. It emphasizes excellent after-sales service, a cornerstone of the Company's operations.
- Expanding the Customer Base to Other Potential Partners: The Company aims to diversify its customer base by reaching out to other potential partners who can provide opportunities for business growth.
- Establishing Long-term Business Partnership Agreements: The Company seeks to secure its relationships with key customers through long-term contracts, ensuring they continue using its products and services.
This also includes regular inspections of installation quality and maintenance of advertising media, as well as the use of technology to monitor screen status in real time, helping to minimize potential impacts on brand image and customer confidence.
The Company ensures that its customers' credit quality and debt repayment capability are analyzed. It regularly reviews the financial status of its customers and makes adjustments appropriate to the circumstances. The risk from foreign exchange rate volatility is likely to have a limited impact on the Company as almost all of its revenues are in Thai Baht. However, to mitigate the potential effects of foreign exchange fluctuations, especially in cases where there might be changes in the value of the Thai Baht against foreign currencies, the Company will manage its foreign currency liabilities to match the revenue generated in foreign currencies. This risk management activity is conducted under the supervision, approval, and monitoring of the Risk Management Committee to ensure compliance with policies and to minimize impacts to an acceptable level for the Company.
Given the risks associated with regulatory changes due to climate change, which is a significant concern for the Company in addressing global warming issues, the Global Climate Risk Index of 2017 ranked Thailand as one of the top ten countries most affected by climate change. In response, the Thai government announced a "National Reform Plan" mandating relevant governmental agencies to develop climate change laws to be enforced within 3 to 5 years. These laws aim to create economic incentives for the private sector to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and encourage public behavioural changes by developing mass transit systems and reducing plastic bag use. However, the mechanisms and enforcement methods for these new policies and regulations remain unclear, posing a risk that could alter business operations. Nevertheless, the Company has strategies to manage risks from climate change:
- Maximizing Resource Efficiency: Using resources such as high-quality light bulbs, energy, and water as effectively as possible in the production process, following the principles of the circular economy to reduce waste.
- Operational Projects: Assessing energy efficiency across all business units to identify appropriate technology uses and employing high-quality light bulbs to reduce electricity consumption directly affecting greenhouse gas emissions.
- Registering for the Thailand Voluntary Emission Reduction Program (T-VER): Preparing for changes in laws related to climate change, where the reduced or sequestered greenhouse gases (carbon credits) can offset emissions, aiding the transition to a low-carbon society.
- Analyzing and Managing Financial Risks Related to Climate Change: This includes both physical risks and risks associated with regulatory changes, aligning with the guidelines of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
- Setting a Climate Strategy for the Company: This should include targets for climate management, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 15% by 2032.
- Engaging and Partnering with Internal and External Stakeholders: Collaborating on energy management and climate change initiatives.
With regard to risks arising from changes in laws or regulations related to billboard installation or the permitting process in public areas—which may impact the implementation of new projects—the Company manages such risks by actively monitoring and analyzing draft legislation under government consideration. This enables timely preparation and adjustments to business plans and operations. Additionally, the Company engages with relevant stakeholders, including advertising associations and government agencies, to propose recommendations and exchange policy-related views.
The Company's risk management strategy focuses on monitoring global trends, new regulations, and the operations of other businesses in the same industry. It assesses the sustainable business framework that considers Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors and manages uncertainties along the value chain by integrating sustainable risk concepts into the "PLANB Enterprise Risk Management Framework," which aligns with the COSO: Enterprise Risk Management Framework. The main components include:
- Governance Structure: Encompassing all levels from the Company board, sustainability and governance committees, audit committee, executive committee, business sustainability development team, risk management team, and business line risk coordinators.
- Understanding Business Context and Strategy: Every unit works closely to understand, analyze, monitor, and communicate risk factors and future trends that could impact business operations or organizational strategy.
- Integrated Risk Management Process: Important risks are assessed across the organization, business groups, or functional levels; strategies for managing these risks are established, and new business opportunities are created. This process aligns with the sustainable development strategy and principles foundational to PLANB’s sustainability efforts.
- Communication, Reporting, and Evaluation: Continuous sustainability and risk management at all levels, from functional and subsidiary to business group and organizational.
- Culture of Sustainability and Risk Management: Educate the Company’s directors, executives, and employees at all levels about sustainable development and risk management through training, orientation, and the dissemination of information via newsletters. This promotes discussion or feedback on sustainable development and risk management, fostering understanding and sharing knowledge of PLANB's sustainable development with employees and stakeholders, such as partners and customers.
The Company manages social risks that may arise from operations in public areas, particularly in the event of complaints from local communities, by continuously assessing the social impact of its business activities. This includes receiving and addressing community feedback, as well as screening advertising content to ensure it does not conflict with public morals or societal values.
Sustainability Risks
The Company actively pursues sustainable business conduct, stressing good corporate governance and sufficient and proper internal control processes. The Company established a clear Anti-Corruption Policy covering all its activities and undertakings. Corruption and guidelines for corruption-prone activities are well-defined and communicated with internal and external parties.
Note that the Company is concerned with the risk of corruption from its activities and requires that this risk be examined, assessed, and prevented. Accordingly, the Company issued control and monitoring measures for activities with potential corruption risk to ensure that its undertakings are honest and transparent and to avoid corruption. Furthermore, communication channels were put in place for stakeholders to blow the whistle, send suggestions and file complaints related to corruption directly with the Audit Committee. In addition, the Company is also a certified member of the Thai Private Sector’s Collective Action Coalition Against Corruption (CAC). Finally, the Company requires all employees to assess their knowledge and understanding of the Code of Conduct, and 100% of employees must pass the assessment to encourage all employees to be fully aware of the Code of Conduct and foster employees' work ethics.
Climate change is expected to increase the frequency, intensity, and impact of certain extreme weather events. The ensuing effects of severe weather, such as flooding, extreme heat, and heavy rainfall, could increase business operating costs due to physical damage and the need to restore and repair property and infrastructure. Moreover, there could be business interruptions. These impacts may lead to direct and indirect costs from physical damages, asset recovery, infrastructure repairs, and business disruption losses, likely affecting PLANB's outdoor advertising business. Furthermore, climate change risks could lead to higher operating costs, such as flood events or heavy rain, causing damage to the company's outdoor advertising structures and increased operational expenses. High temperatures might also reduce vinyl products' lifespan in outdoor advertising, leading to more frequent and costly replacements and maintenance.
PLANB is actively contributing to the prevention of climate change and extreme weather conditions by initiating various environmental management projects to conserve energy use and ensure efficient waste management. The Company has implemented the following key risk management measures:
- Continual Monitoring of Climate Change Impacts: The Company is committed to monitoring the effects of climate change, considering it part of its risk management and governance processes. It has also developed an Organizational Business Continuity Plan (BCP) and disaster recovery plans to manage unfavourable weather events and respond to business interruptions.
- Adherence to Corporate Environmental Policy: All business units must strictly follow the Company's environmental policy. This includes implementing environmental management systems like ISO 14001, applying the 3Rs principle (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle), managing and reducing water usage, managing and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and initiating corporate and product-level Carbon Footprint projects.
- Use of Modern and Energy-efficient Technology: High-quality LED lighting decreases resource and energy consumption and reduces greenhouse gas emissions, thus lowering operational costs and enhancing production efficiency and effectiveness.
- Environmental and Sustainable Development Practices with Partners: Managing and aligning with partners’ environmental and sustainable development practices.
Driven by increasing pressure from government policies, investors, and global societal expectations, the transition toward a low-carbon society—such as the establishment of Net Zero targets or the implementation of carbon pricing mechanisms (e.g., Carbon Tax / CBAM – Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism)—is accelerating and may impact business operations within the next 3–5 years. For companies in the media industry, such as out-of-home (OOH) advertising, this transition may result in pressure from clients seeking to reduce the carbon footprint of their advertising activities, or in additional costs related to upgrading media technology to improve energy efficiency. Without sufficient preparation in ESG readiness and sustainable innovation, the Company may risk losing long-term competitiveness.
Operational Risks
At present, the Company has set a goal to enhance work efficiency through digital technology to promote the cost-effectiveness of business. This requires that the Company rely more on technology. Therefore, an internet connection may threaten the Company at any time. To prepare the organization to ensure cybersecurity and stability of the Company’s computer systems used in conducting business and to comply with international standards on cybersecurity and the Cybersecurity Act B.E.2562 (2019). In 2021, the Company issued multiple strict measures to actively and passively manage risks, including:
- - Formulate a defined cybersecurity policy for the group of companies and set up a working team directly responsible for cybersecurity in the short and long run.
- - Training employees on potential cyber threats and guidelines to prevent/tackle the incidents by themselves to alleviate damages and minimize impacts.
- - System testing and rehearsals of IT system recovery in case of cyber threats.
As the Personal Data Protection Act B.E. 2562 (2019), which comes into force on 1 June 2022 (“Personal Data Protection Laws”), the Company has full awareness of the importance of Personal Data Protection Laws, including rules and regulations issued by the Personal Data Protection Committee (“Committee”) as the guideline for Person-al Data Protection Laws compliance, the Company, therefore, set up the personal data protection working team to responsible for the privacy policy, plan, and internal procedure of the Company to be following Personal Data Protection Laws, including any relevant rules and regulations, and updating policies and regulations of the Company involving personal data protection to be present considering Personal Data Protection Laws and its amendment. In addition, the Company has set up an individual data collection system to prevent the risk of data leaking and promptly mitigate the damages that may occur. Furthermore, if the Company receives any complaint or request from the data subject, the system can track data, documents, and information on time. The Company has provided the operational plan which shall be used by employees of the Company and the subsidiaries of the Company when collecting the personal data from the data subject necessary that includes the process to delete or destroy the personal data when it is unnecessary to maintain considering the purpose of the collection, to respond to the data subject’s request to remove, delete or modify its data possessed by the Company and to inform partners and customers to acknowledge the privacy policy of the Company to effectively working together and to be following the Personal Data Protection Laws and guidelines issued by the Committee.
The rapid pace of technological change, coupled with shifting consumer behavior—such as increased consumption of digital media through social media platforms, video streaming, mobile applications, and on-demand content—may lead to reduced attention and time spent on traditional media, particularly television and out-of-home (OOH) advertising. If the Company is unable to innovate or adapt its brand communication strategies in a timely manner to respond to new consumer behaviors, it may adversely impact its competitiveness, advertising revenue, and ability to retain clients in the long term.
This risk is considered a medium-to-long-term risk over the next 3–5 years, as it is driven by macro-level changes in the economy, society, and environment. Nevertheless, the Company has continuously developed advertising screen formats to align with evolving consumer behavior and communication preferences.Furthermore, the Company has developed the MAGNETIC Measurement system, a real-time data analytics tool that enables accurate evaluation of campaign performance. Insights derived from the system are used to analyze consumer behavior, allowing brands to plan and create campaigns that are highly targeted and effectively meet customer needs.
The global trend toward aging societies, including in Thailand, is significantly reshaping the labor force structure. Companies that rely heavily on traditional skill sets or a large number of younger workers may face labor shortages in the future.At the same time, the behavior and expectations of the new generation of workers—such as Gen Z—are notably different. They place higher value on flexibility, meaningful work, and social impact, which could affect the Company’s ability to attract and retain talent if it does not adapt its organizational culture, skills development systems, or job design accordingly.
Although artificial intelligence (AI) and big data play a critical role in enhancing business efficiency, in the near future, the risk of unethical AI use or algorithmic bias may undermine the trust of customers, partners, and the general public. Moreover, lack of transparency in data usage could violate personal privacy rights or breach increasingly stringent regulations—such as the EU AI Act or emerging AI ethics guidelines. If the Company does not establish appropriate governance frameworks for AI and data management, it may face reputational, legal, and trust-related risks.
In today’s environment, where information spreads rapidly and widely through social media, many consumers are more inclined to believe content that aligns with their personal beliefs rather than objective facts (confirmation bias). It is increasingly difficult to distinguish between factual information and misinformation or fake news. Such behavior presents a growing challenge for brands in communicating corporate values, sustainability efforts, and ethical commitments in a credible manner—especially in the face of viral social movements that can lead to brand "cancellation," even when based on incomplete or misleading information. For companies in the advertising and brand-awareness business—such as Plan B—this shift presents a material risk that may affect:
- - The ability to control media content in public spaces
- - The level of trust clients place in brands using the Company’s media platforms
- - The likelihood of brands becoming targets of online backlash or having their intentions misrepresented
Plan B recognizes that today’s business landscape is rapidly evolving due to a range of factors across economic, social, technological, and environmental dimensions—all of which have implications for medium- to long-term business operations. Emerging risks such as increasingly stringent ESG regulations, demographic shifts, and changes in consumer behavior in an age of information overload may not yet have a clear short-term impact. However, without proper preparation, these risks could lead to loss of competitiveness, rising costs, and potential reputational damage in the future.
To mitigate the impact of such risks and enhance business resilience, the Company is in the process of developing an emerging risk management plan, with clear and actionable approaches as follows:
1. Emerging Risk Monitoring Framework
The Company will establish a systematic mechanism for monitoring emerging risks by assigning responsibility to either the Risk Management Working Group or a dedicated Strategic Risk Unit. This unit will be tasked with tracking and analyzing early warning signals from both internal and external sources, such as:
- Changes in international regulations
- Government policies on environmental and labor issues
- Sudden shifts in consumer behavior
- Macroeconomic trends and market volatility
This mechanism will enable the Company to promptly identify risks and proactively prepare for potential impacts before they affect the business.
2. Prioritization & Materiality Assessment
Once potential risks are identified, the Company will conduct a risk assessment in accordance with the COSO Enterprise Risk Management framework, taking into account both the likelihood of occurrence and the impact on the organization. Risks will then be prioritized based on their severity and relevance to the Company’s strategic plan, allowing for appropriate planning and resource allocation.For example:
- If it is found that younger generations in the workforce place greater importance on ESG values than financial compensation, the Company will promptly revise its employer branding strategy to meet evolving expectations.
3. Risk Response Plan
To address potential risks, the Company will establish a response framework that includes both:
- Preventive Measures such as revising procurement policies and selecting partners with established ESG systems
- Mitigative Actions such as implementing technology backup plans and providing reskilling programs for employees
These response strategies will be integrated into the Company’s Business Continuity Plan (BCP) and the overall Enterprise Risk Management Plan.
4. Strategic Integration
The Company will communicate information on emerging risks and corresponding response strategies to all relevant stakeholders—ranging from the Board of Directors and senior management to supervisors and operational staff. This ensures organization-wide awareness of potential risks and fosters active participation in the risk management process. In addition, insights from emerging risks will be integrated into the Company’s strategic planning to enhance business flexibility and enable timely adaptation to a rapidly changing external environment.
5. Review and Adaptation
To ensure effective and up-to-date risk management, the Company will review and update its emerging risk management plan at least once a year, or upon the occurrence of significant events—such as outbreaks of emerging diseases, natural disasters, or changes in national and international regulations. The Company will also emphasize post-incident review and continuous improvement of risk management approaches, in order to enhance organizational preparedness and resilience across all scenarios.
The Company has set policies and a code of conduct for suppliers in Procurement and hiring to ensure that our suppliers follow our guidelines for sustainable business operations per the Company's expectations. Furthermore, The Company also sets a Code of Conduct covering guidelines for supplier screening and a section to identify suppliers with significant or high ESG risks and for following up and examining suppliers. Suppliers are expected to adhere to ethical and operational principles that prevent impacts on the community and the environment while protecting workers and society's occupational health and safety.
The company has established a Supplier Code of Conduct to ensure that the supply chain management is appropriate and effective. This code sets out sustainable business practices between the company and all its suppliers, establishing standards and practices for suppliers to follow throughout their operational processes. The Supplier Code of Conduct aims to develop standards in five main areas:
The company has a policy for the equitable and fair selection and procurement of suppliers that also considers the company's best interests, based on the foundation of receiving fair returns for both parties. This is aligned with sustainable development through building trust with stakeholders in all sectors via excellent, transparent, and fair supplier selection and procurement. This is under procurement management principles and practices according to international standards.
- Establish criteria for evaluating and selecting suppliers, with strict screening, to ensure fair business practices and no violation of human rights.
- Supplier selection and procurement should be based on quality, price, quantity, service, and responsiveness while also considering their involvement in social and environmental responsibilities.
- Ensure that the selection and procurement of suppliers are transparent, fair, and verifiable, strictly adhering to relevant regulations, standards, and laws, including comprehensive economic, social, and environmental risk considerations. The company also prioritizes combating all forms of unfair competition and strictly prohibits dishonest benefits in dealings with suppliers.
- Procurement processes must not exploit suppliers. They must provide complete, accurate, precise, and disclosed information, treat all suppliers equally, and consider their feedback and suggestions for operational improvements.
- Strictly adhere to agreed-upon conditions; if unable to meet any conditions, promptly inform the supplier to explore solutions promptly jointly.
- Consider suppliers based on environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance (Environmental, Social & Governance: ESG), and supervise suppliers to adhere to the company’s supplier practices as part of sustainable supply chain management.
- Focus on supplier management, build good relationships, and enhance their capabilities for joint sustainable development.
- Integrate sustainability into procurement processes by setting criteria for selecting new and current suppliers, including assessing purchases, evaluating key and at-risk suppliers on-site for potential sustainability risks, and continually addressing complaints.
- Manage the knowledge base between the company and suppliers, push for the use of technology to enhance procurement capabilities, and strive for excellence within the company.
All company executives and employees are required to support, promote, and strictly adhere to the procurement policies and management framework. They must uphold human dignity, equality, and fairness and avoid discrimination based on physical or mental differences, race, nationality, religion, gender, age, education, or any other factor.
The company places great importance on fairly and appropriately selecting suppliers to ensure the process is conducted according to established criteria. The company sets these criteria by considering various qualifications to categorize and select suppliers. This includes assessing risks related to economic, social, and environmental factors from suppliers. The criteria for selecting suppliers are as follows:
- Suppliers must have verifiable business premises.
- Suppliers must have reliable personnel, machinery, equipment, products, services, warehousing, financial status, and a trustworthy operational history.
- Suppliers should have a satisfactory performance record, including product quality, service delivery, timeliness, after-sales service, warranties, or other agreed-upon transaction conditions.
- Suppliers must strictly adhere to relevant regulations, rules, and laws, conduct their business fairly and transparently, have no conflicts of interest with the company, and have no history of trade bans due to fraudulent activities or a history of abandoning work or being blacklisted by government or private entities.
- Suppliers must demonstrate a commitment to social and environmental responsibility, covering human rights, employee and labor care, business ethics, and compliance with environmental laws.
The selection of new and current suppliers must adhere to the criteria established by the company, focusing on evaluating qualifications for selecting and categorizing suppliers. This process also aligns with the company's procurement policies, supplier relations practices, and supply chain management policies. Additionally, suppliers must demonstrate a commitment and responsibility to society and the environment, including careful human rights considerations, employee and labor care, business ethics, and compliance with environmental laws.
The Company adopts a centralized procurement system to enhance cost management efficiency, quality control, and transparency in the sourcing process. A clear supplier segmentation framework is in place for Tier 1 suppliers (those doing business directly with the Company), classifying them into three groups: Critical Suppliers, Non-Critical Suppliers, and General Suppliers. Each group is subject to tailored risk assessment and management approaches based on its level of importance and impact on the Company’s operations.
However, to ensure more comprehensive procurement management, the Company has expanded its scope to include critical non-tier 1 suppliers—suppliers in the next tier of the supply chain, such as key raw material manufacturers or subcontractors that affect the delivery performance of critical suppliers. Although these suppliers do not have a direct business relationship with the Company, they are vital to business continuity and may pose supply chain risks if any issues arise.
To ensure efficient and comprehensive procurement management, the Company has established a systematic set of criteria for supplier segmentation. This classification is based on factors such as risk level, contract value, strategic importance, and substitutability, with tailored evaluation approaches defined for each group, as follows:
- Critical Supplier These are suppliers with high contract value or spending volume, low substitutability, and high strategic importance to revenue generation. They are considered to carry high or very high risk. The Company requires an annual performance evaluation for this group using the Vendor Evaluation Form, on-site audits, and sustainability performance assessments. This group typically includes LED display product suppliers.
- Non-Critical Supplier These are suppliers not classified as critical, with medium spending levels or low contract value, and moderate to low risk. The Company conducts annual performance evaluations using the Vendor Evaluation Form and Vendor Self-Assessment Questionnaire. This group typically includes construction contractors, spare parts and equipment providers, IT services and equipment, and consumable materials.
- General Supplier These are suppliers not classified as either critical or non-critical, with relatively low transaction volumes, minimal business risk, and no significant management complexity. These suppliers typically offer easily substitutable products or services and have multiple sourcing options. The Company conducts case-by-case evaluations as appropriate, without requiring annual assessments due to the low level of business impact.
- Critical Non-Tier 1 These are suppliers that do not supply goods or services directly to the Company but play a key role in the supply chain of critical suppliers—for example, manufacturers of essential components or upstream suppliers to critical vendors.
Risk Management and Assessment Approach for Critical Non-Tier 1 Suppliers To effectively develop risk management plans and collaborate appropriately with this supplier group, the Company has established the following approach for monitoring and managing relationships with Critical Non-Tier 1 suppliers:
- Coordinate with Tier 1 suppliers to obtain supply chain information such as a list of key subcontractors or frequently used raw material manufacturers.
- Conduct preliminary risk assessments through indirect evaluation using questionnaires related to quality, environmental management, labor law compliance, and sustainability practices, in collaboration with relevant Tier 1 suppliers.
- Monitor and review risks jointly with Tier 1 suppliers on a periodic basis, especially when early warning signals arise—such as delivery delays, quality issues, or human rights violations within the supply chain.
- Integrate risk monitoring into existing On-site Audits or Supplier Meetings of Tier 1 suppliers by including additional assessment items related to subcontractors or secondary suppliers in the evaluation form.
A systematic approach to identifying and managing Critical Non-Tier 1 suppliers enables the Company to conduct comprehensive risk assessments across the entire supply chain (End-to-End Supply Chain Risk Management) and to develop appropriate response plans. This supports business continuity, reduces the likelihood of unforeseen disruptions, and promotes long-term sustainability for both the Company and its suppliers at all levels.
All new suppliers are required to accept and comply with the Company's Supplier Code of Conduct to ensure mutual understanding and confirmation of agreement. This acceptance is also seen as a commitment to joint sustainable development. In 2024, all suppliers acknowledged and accepted the Supplier Code of Conduct, which outlines the Company’s business ethics and expectations for supplier practices.
The Company conducts an annual supplier evaluation to analyze relevant information and identify areas for improvement in collaboration with its suppliers. This process supports the development of sustainable business practices for both the Company and its partners. The Company’s supplier evaluation is divided into two main categories: Supplier’s Risk Assessment and Supplier’s Performance Assessment. The details of each category are as follows:
Supplier’s risk assessment
The Company mandates a risk assessment for suppliers to rank potential risks that could impact the business operations. This assessment is based on company-defined criteria, covering three crucial aspects: economic, social, and environmental dimensions.
| Risk Factors | Risk Management Guidelines |
| Economic | |
| Financial status and stability of suppliers |
|
| Suppliers with high transaction value |
|
| Social | |
| Child labor, illegal migrant labor, or violations of human rights |
|
| Occupational health and safety |
|
| Environmental | |
| Environmental protection and waste management |
|
The assessment is based on the likelihood of risk occurrence and the severity of impact, using both quantitative and qualitative criteria as a foundation for evaluating various risks. The assessment is categorized into four levels, as follows:
| Likelihood and Impact | Description | Level |
| Very High | Once per month or more frequently / More than THB 10mn | 4 |
| High | Once every 1-6 months, up to 5 times / Between THB 5-9mn | 3 |
| Moderate | Once every 1-3 years / Between THB 1–4mn | 2 |
| Low | Once every 4-5 years / Not more than THB 1mn | 1 |
Supplier’s performance assessment
The Company conducts ongoing evaluations of supplier performance to ensure their ability to meet business requirements with quality and sustainability. The assessment covers four key areas:
- Product and Service Quality: Assessed based on the standard of products and services delivered, including specification compliance, consistency of quality, warranty provisions, and the rate of complaints or product defects during use.
- Complete and On-Time Delivery: Evaluated by analyzing the timeliness of deliveries according to the agreed schedule and the supplier’s ability to fulfill each order completely. Effective stock and logistics management is a critical factor in this area.
- Coordination and Management Efficiency: Assessed based on communication effectiveness, responsiveness to issues, adaptability to changing circumstances, and the ability to manage projects systematically and professionally in collaboration with the Company.
- Social and Environmental Responsibility: Suppliers must operate with consideration for environmental and social impacts—for example, efficient resource use, compliance with environmental laws, fair labor practices, and participation in CSR initiatives. Performance may be verified through certifications or meeting ESG assessment standards from external bodies.
| METHODS FOR EVALUATING SUPPLIERS | ||
| SUPPLIER GROUP | DOCUMENT REVIEW AND SELF-ASSESSMENT VIA ONLINE SYSTEM | ON-SITE EVALUATION |
| Critical Supplier | ✔ | ✔ |
| Non-Critical Supplier | ✔ | |
| General Supplier | ||
| Critical Non-Tier 1 | ✔ | |
The Company conducts environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risk assessments for key suppliers through Vendor Self-Assessments and regular On-Site Audits to ensure that suppliers operate ethically, transparently, and in compliance with labor, human rights, and environmental laws. In 2024, the Company conducted ESG risk assessments of key suppliers and found that no key suppliers were identified as having ESG-related risks.
| SUPPLIER RISK ASSESSMENT | ||
| ECONOMIC DIMENSION | SOCIAL DIMENSION | ENVIRONMENTAL DIMENSION |
|
|
|
PLANB has established an annual process to identify key suppliers in order to develop effective supplier relationship management strategies. This process supports prioritization in resource allocation and risk management. Key factors considered in identifying critical suppliers include: the supplier’s maturity in sustainable business practices, alignment of the supplier’s business objectives with Plan B’s goals, involvement with critical materials, irreplaceability, and the degree of mutual dependency between Plan B and the supplier. These considerations enable Plan B to proactively identify and mitigate potential risks across its procurement process and throughout the supply chain.
- 100% of key suppliers are aware of the supplier code of conduct
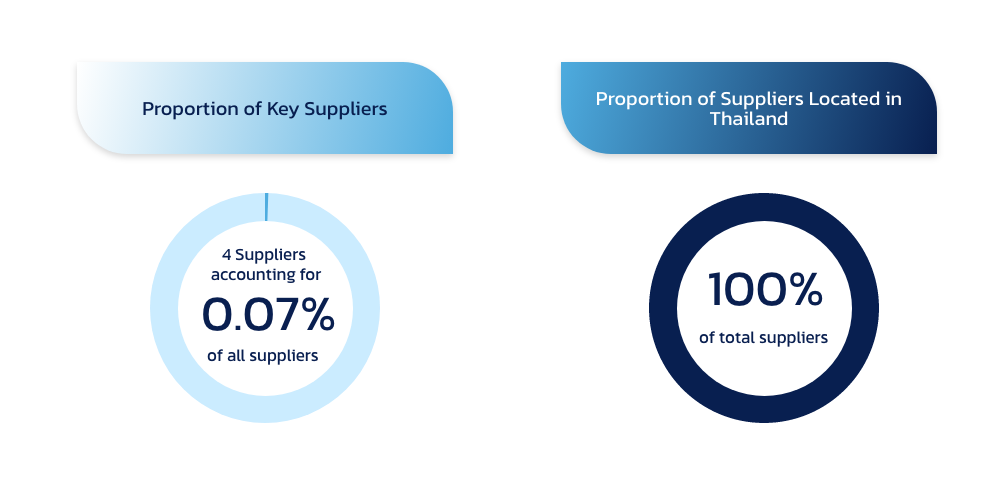
PLANB considers sustainability factors throughout the procurement process and mandates that suppliers adhere to specific supplier guidelines and undergo strict screening, considering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors and quality audit processes. These are enforced for 100% of PLANB's suppliers. PLANB also sets sustainability as a criterion in evaluating supplier qualifications, the bidding process, and supplier performance assessment. PLANB has specified requirements for key suppliers and strategic supplier groups to enforce critical policies that align with PLANB’s standards and ensure that PLANB’s indirect suppliers comply with PLANB’s sustainability requirements.
- 100% of PLANB's Tier 1 suppliers acknowledge and accept the supplier guidelines
The company has established a procurement code of conduct for suppliers to define guidelines for sustainable business practices between the company and its suppliers. This sets standards and practices for transparency, equality, and fairness throughout the cooperative process, covering environmental standards, human rights, occupational health, safety, and ethical principles. The company also encourages its suppliers to apply these practices with their suppliers, promoting sustainability throughout the value chain and fostering long-term value creation with partners.
PLANB places great importance on conducting business in a sustainable manner and is committed to serving customers and business partners with fairness, transparency, and full compliance with corporate governance principles and relevant regulations.
PLANB takes into account key factors affecting business liquidity and cash flow management. The Company has established a payment policy whereby payments to suppliers are made within 30–90 days, depending on the type of goods or services provided—such as advertising services or media production. Billing and payment transfers for general suppliers follow the Company’s standard accounting cycle and payment procedures.
However, credit terms and payment periods for certain vendors, suppliers, contractors, or service providers of the Company—or those of its subsidiaries—may differ from the aforementioned general policy. These variations depend on the nature of the business, type of goods, raw materials, and specific services provided, as mutually agreed upon by the Company or its subsidiaries and each respective vendor, supplier, contractor, or service provider.
The Company ensures that such agreements are made in alignment with established standards and based on the principle of fairness to all suppliers. Considerations include market conditions, industry benchmarks, and the terms of individual business agreements.
| LIQUIDITY RATIOS | 2023 | 2024 |
| Current Ratio (times) | 1.02 | 1.20 |
| Quick Ratio (times) | 1.02 | 1.19 |
| Average Collection Period (days) | 108.9 | 116.6 |
| Average Payment Period (days) | 109.8 | 101.4 |
According to the Company’s policy, the standard payment period for suppliers is set at 30-90 days. However, in 2023 and 2024, the actual average payment periods were 109.8 days and 101.4 days, respectively—exceeding the policy range. The primary reason for this deviation is occasional delays in payments from certain customer segments, particularly government agencies. These delays are typically due to budgetary constraints, complex disbursement procedures under bureaucratic systems, or political uncertainty.
Although the Company has been affected by external factors beyond its control, the trade receivables turnover ratio remains at a manageable level and has not had a material impact on the Company’s overall performance. The Company continues to closely monitor and manage credit risk, while also maintaining liquidity with prudence, ensuring the ability to operate securely and sustainably under all conditions.
The Company recognizes the critical importance of cybersecurity and the stability of its information network, which face increasing risks from data theft and increasingly complex forms of cybercrime. Such threats can impact not only economic, social, and environmental security, but also the trust and credibility the Company holds with its partners and customers. Furthermore, the Company places strong emphasis on strict compliance with both domestic and international laws and regulations related to cybersecurity and data privacy to prevent cyber threats and mitigate the potential impact of data breaches. In response, the Company is committed to operating in full accordance with applicable laws and global standards, and has established comprehensive policies and practices to strengthen overall information security, as outlined below:
1. Information Security Policy Development
The Company has established an Information Security Policy that applies to all employees and relevant parties acting on behalf of the Company. This policy serves as a framework to guide the implementation of information security practices that align with applicable legal requirements and regulatory standards. The key components of the policy include:
- The Company’s information security structure
- Personnel security and information asset management
- Access control to systems and data
- Data encryption and physical environment management
- Information security incident management
- Business Continuity Management (BCM)
This policy is subject to periodic review and compliance audits conducted by both internal and external auditors to ensure its continued relevance and alignment with regulatory requirements.
2. Development of Business Continuity Plan and Information System Recovery Plan to ensure data availability and effective management in the event of disruptions to critical business processes. These plans are essential to maintaining operational readiness and minimizing the impact of unforeseen interruptions.
3. Cybersecurity Training and Basic Computer Troubleshooting Awareness for all employees to enhance their knowledge and awareness of cybersecurity, cyber threats, and preventive and remedial measures for basic computer issues. In 2024, the training was conducted in an online format, with a total of 100 participants.
4. Plan B places great importance on protecting the privacy of personal data for all stakeholder groups, including customers, employees, business partners, suppliers, and shareholders The Company has established a Privacy Policy to declare its commitment to protecting personal data in alignment with the Personal Data Protection Act B.E. 2562 (2019). Additionally, the Company provides training on the legal requirements under the Act to raise awareness among employees. Relevant training courses have also been provided to members of the Board of Directors to ensure preparedness and enhance their understanding ahead of the law's enforcement. PLANB uses customer data strictly for the purposes specified in the Privacy Policy and/or for which consent has been obtained, in accordance with legal requirements.
Information Security and Data Privacy Results
The Company is committed to developing systems and managing information security continuously. For example, to ensure that data breaches are 100 percent wholly prevented according to the goal, whether it be data leakage or loss.
| PERFORMANCE | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Number of complaints from external and confirmed by PLANB’s internal | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Number of complaints from the Corporate Governance Committee | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Number of breaches of information security or other cybersecurity incidents | 0 | 0 | 0 |